Type 1diabetes in children can be controlled if right diabetes management techniques are followed by parents. Read on to know more about the symptoms of Type 1 diabetes in children and tips for management of Type 1 diabetes in children. Diabetes is a metabolism disorder in which the blood sugar levels become higher than normal. Type 1 diabetes used to earlier be known as juvenile diabetes. Although it can strike at any age, it is most often diagnosed in children, adolescents and young adults. In this articleWhat is Type 1 DiabetesAbout Type 1 DiabetesSymptoms of Type 1 DiabetesManagement of Type 1 Diabetes in ChildrenLiving with Type 1 DiabetesWhat is Type 1 Diabetes Most of the food which we eat is broken down into glucose. Glucose is a type of sugar present in the bloodstream. Food which we eat is digested and enters the bloodstream in the form of glucose. This glucose is then carried to the cells for growth and energy. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas which helps to transport the glucose to the cells. Without the help of this hormone, glucose cannot enter our cells. Type 1 diabetes occurs when the body stops producing insulin. The level of blood glucose becomes very high leading to a condition called hyperglycemia. About Type 1 Diabetes In this form of diabetes, the person has lost his or her beta cells which are present in the pancreas to produce insulin. The person’s own body has destroyed the ability to produce insulin. This form of diabetes is not preventable and cannot be blamed on the person’s lifestyle. Being fit or unfit, thin or fat is no way going to make a difference to his or her chances of developing Type 1 diabetes. In fact a large number of people are quite healthy at the onset of Type 1 diabetes. By exercising more or eating healthy, you cannot reverse or prevent Type 1 diabetes. In majority of the cases, this type of diabetes affects the person before he has reached the age of 40. Symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes When the blood sugar is high or a person has Type 1 diabetes, he may first notice these symptoms:Feeling tired or exhaustedFeeling hungryExcessive thirstFrequent urinationExperiencing weight loss without tryingBlurred eyesightNumbness or a tingling sensation in feetSometimes a person will have no symptoms before they are diagnosed with diabetes. Sometimes such warning symptoms which make the person severely sick like the ones below might also be signs of Type 1 diabetes or very high blood sugar. Deep and rapid breathingDryness of skin and mouthFlushed faceFruity odor of the breathNausea or vomiting, unable to keep down liquidsStomach pain Management of Type 1 Diabetes in Children You can monitor and control glucose levels in children in the following ways. You need to:- Testing Blood Sugar Levels – You can test the blood sugar levels. Keep a check on your child’s blood sugar levels a few times every day by testing a small sample. Insulin Injections – give insulin injections to your child at right time. Providing a Balanced, Healthy Diet – Children with Type 1 diabetes must eat a healthy, balanced diet. They must keep a watch on the amount of sugar and starch intake in their food and the timing of their meals. Staying Fit – Regular exercise will help to control blood sugar levels. It will also help to prevent some of the long term health problems that can arise due to diabetes like heart disease. Living with Type 1 Diabetes Children with Type 1 diabetes may often feel frustrated, angry or scared. Kids or teens may not be able to follow a lifestyle like their peers. Smaller children may not understand why they have to take insulin injections or blood tests and may be uncooperative. Living with diabetes is a challenge and especially for children it is all the more difficult. Doctors and the health care team can provide parents and children support and help the child to cope and live with diabetes.
Type 1diabetes in children can be controlled if right diabetes management techniques are followed by parents. Read on to know more about the symptoms of Type 1 diabetes in children and tips for management of Type 1 diabetes in children. Diabetes is a metabolism disorder in which the blood sugar levels become higher than normal. Type 1
diabetes used to earlier be known as juvenile diabetes. Although it can strike at any age, it is most often diagnosed in children, adolescents and young adults.
What is Type 1 Diabetes
Most of the food which we eat is broken down into glucose. Glucose is a type of sugar present in the bloodstream. Food which we eat is digested and enters the bloodstream in the form of glucose. This glucose is then carried to the cells for growth and energy.
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas which helps to transport the glucose to the cells. Without the help of this hormone, glucose cannot enter our cells. Type 1 diabetes occurs when the body stops producing insulin. The level of blood glucose becomes very high leading to a condition called hyperglycemia.
About Type 1 Diabetes
In this form of diabetes, the person has lost his or her beta cells which are present in the pancreas to produce insulin. The person’s own body has destroyed the ability to produce insulin. This form of diabetes is not preventable and cannot be blamed on the person’s lifestyle.
Being fit or unfit, thin or fat is no way going to make a difference to his or her chances of developing Type 1 diabetes. In fact a large number of people are quite healthy at the onset of Type 1 diabetes. By exercising more or eating healthy, you cannot reverse or prevent Type 1 diabetes. In majority of the cases, this type of diabetes affects the person before he has reached the age of 40.
Symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes
When the blood sugar is high or a person has Type 1 diabetes, he may first notice these symptoms:
- Feeling tired or exhausted
- Feeling hungry
- Excessive thirst
- Frequent urination
- Experiencing weight loss without trying
- Blurred eyesight
- Numbness or a tingling sensation in feet
Sometimes a person will have no symptoms before they are diagnosed with diabetes. Sometimes such warning symptoms which make the person severely sick like the ones below might also be signs of Type 1 diabetes or very high blood sugar.
- Deep and rapid breathing
- Dryness of skin and mouth
- Flushed face
- Fruity odor of the breath
- Nausea or vomiting, unable to keep down liquids
- Stomach pain
Management of Type 1 Diabetes in Children
You can monitor and control glucose levels in children in the following ways. You need to:-
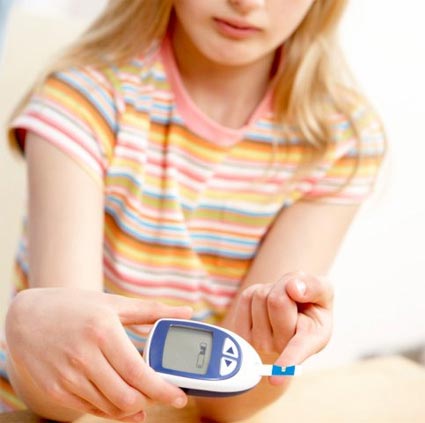
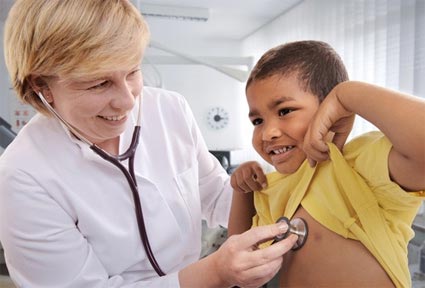
Testing Blood Sugar Levels – You can test the blood sugar levels. Keep a check on your child’s blood sugar levels a few times every day by testing a small sample.
Insulin Injections – give insulin injections to your child at right time.
Providing a Balanced, Healthy Diet – Children with Type 1 diabetes must eat a healthy, balanced diet. They must keep a watch on the amount of sugar and starch intake in their food and the timing of their meals.
Staying Fit – Regular
exercise will help to control blood sugar levels. It will also help to prevent some of the long term health problems that can arise due to diabetes like heart disease.
Living with Type 1 Diabetes
Children with Type 1 diabetes may often feel frustrated, angry or scared. Kids or teens may not be able to follow a lifestyle like their peers. Smaller children may not understand why they have to take insulin injections or blood tests and may be uncooperative. Living with diabetes is a challenge and especially for children it is all the more difficult. Doctors and the health care team can provide parents and children support and help the child to cope and live with diabetes.