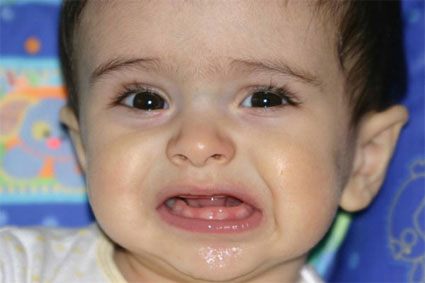
No parent wants her child to develop into a biter. Proper measures should be taken at right time to stop children indulge in biting. Here are signs to distinguish between different types of biting. Almost all children indulge in biting at some point of time. Biting is not unusual behaviour but can become a habit if it is not controlled in the early stages. Biting can also become a dangerous behaviour. A child who bites may be putting herself and her bite victims at risk by exposing them to bacteria and other contagions. A child may indulge in biting for a variety of reasons. If you can determine why the behaviour is occurring, you can implement a suitable disciplinary technique to discourage your child from future biting episodes. Here are some of the reasons why children bite. In this articleAs an experimentAs a sign of frustrationTo escape a threatAs an experiment This is the most common reason for biting, especially in infants. When your baby starts teething, he experiences pain. To combat the pain, the baby will engage in biting just about anything he can get hold of, including other peoples fingers for example. At this stage, you cannot really discourage biting. However, you can provide appropriate alternatives such as teething rings. Babies and young children are also extremely curious. Your child wants to explore the world around him. The easiest way for him to do so is by using his senses of touch, taste, and smell. Sometimes, he will bite you or his caregivers, just to see how it feels. When this occurs, dissuade him from continuing using a firm No. This sends out a clear signal that his behaviour is wrong and should not be repeated. As a sign of frustration Biting due to frustration is largely prevalent in toddlers. At this age, your child is still finding it difficult to verbally express his needs and wants. Sometimes, he may desire attention from a parent or want to play with another childs toy but he cannot voice his desire aloud. As his frustration mounts, he may resort to biting either an adult or another child to get his point across. The main point to remember is that the child is not biting to cause harm. However, this does not excuse his behaviour. If your child has bitten someone, the first step is to tend to the victim. This is especially important if the victim is another child. The next stage is to express disapproval of your childs behaviour. Explain to him that biting is harmful and it hurts others. In addition, help your child express his feelings. Teach him how to communicate when he wants something. Use the positive reinforcement technique. Praise him whenever he expresses his needs in a peaceful manner. Above all, observe your child for any signs of frustration, especially when he is playing with other children. If you think your child is getting frustrated, step in and divert his attention before he lashes out at someone. To escape a threat If another child or a sibling bullies your child, he may use biting as a form of self-defence. Alternatively, he may also resort to biting when he has to deal with a stressful situation in the home. Biting has been observed in young children as a response to their parents divorce or to cope with the death of a loved one. A child who is biting because of stress requires special attention. You can be more loving and more attentive to him so that he does not feel neglected. Again, positive reinforcement is an effective tool to help your child deal with his emotions. If your child is biting because of being bullied, explain to your child that biting is never a solution. In addition, tackle the bullying issue itself to ensure that your child is not victimised. Biting can be caught early and dealt with before it becomes a major issue. If you see your child indulging in this behaviour, do not punish him. Find out why he is biting and act appropriately to discourage him from repeating the behaviour.
No parent wants her child to develop into a biter. Proper measures should be taken at right time to stop children indulge in biting. Here are signs to distinguish between different types of biting. Almost all children indulge in biting at some point of time. Biting is not unusual behaviour but can become a habit if it is not controlled in the early stages. Biting can also become a dangerous behaviour. A child who bites may be putting herself and her bite victims at risk by exposing them to bacteria and other contagions.
A child may indulge in biting for a variety of reasons. If you can determine why the behaviour is occurring, you can implement a suitable disciplinary technique to discourage your child from future biting episodes. Here are some of the reasons why children
bite.
As an experiment
This is the most common reason for biting, especially in infants. When your baby starts
teething, he experiences pain. To combat the pain, the baby will engage in biting just about anything he can get hold of, including other people's fingers for example. At this stage, you cannot really discourage biting. However, you can provide appropriate alternatives such as teething rings.
Babies and young
children are also extremely curious. Your child wants to explore the world around him. The easiest way for him to do so is by using his senses of touch, taste, and smell. Sometimes, he will bite you or his caregivers, just to see how it feels. When this occurs, dissuade him from continuing using a firm 'No'. This sends out a clear signal that his behaviour is wrong and should not be repeated.
As a sign of frustration
Biting due to frustration is largely prevalent in toddlers. At this age, your child is still finding it difficult to verbally express his needs and wants. Sometimes, he may desire attention from a parent or want to play with another child's toy but he cannot voice his desire aloud. As his frustration mounts, he may resort to
biting either an adult or another child to get his point across.
The main point to remember is that the child is not biting to cause harm. However, this does not excuse his behaviour. If your child has bitten someone, the first step is to tend to the victim. This is especially important if the victim is another child. The next stage is to express disapproval of your child's behaviour. Explain to him that biting is harmful and it hurts others.
In addition, help your child
express his feelings. Teach him how to communicate when he wants something. Use the positive reinforcement technique. Praise him whenever he expresses his needs in a peaceful manner. Above all, observe your child for any signs of frustration, especially when he is playing with other children. If you think your child is getting frustrated, step in and divert his attention before he lashes out at someone.
To escape a threat
If another child or a sibling bullies your child, he may use biting as a form of self-defence. Alternatively, he may also resort to biting when he has to deal with a stressful situation in the home. Biting has been observed in young children as a response to their parent's divorce or to cope with the death of a loved one.
A child who is biting because of stress requires special attention. You can be more loving and more attentive to him so that he does not feel neglected. Again, positive reinforcement is an effective tool to help your child deal with his emotions. If your child is biting because of being bullied, explain to your child that biting is never a solution. In addition, tackle the bullying issue itself to ensure that your child is not victimised.
Biting can be caught early and dealt with before it becomes a major issue. If you see your child indulging in this behaviour, do not punish him. Find out why he is biting and act appropriately to discourage him from repeating the behaviour.