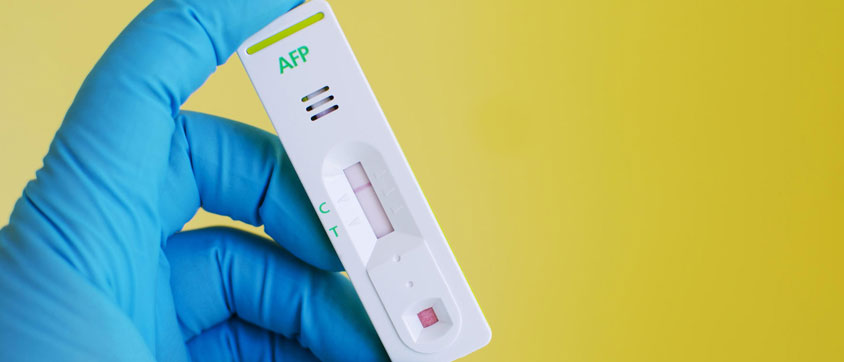
Alpha-Fetoprotein test of AFP test can help to detect birth defects in the baby during pregnancy. Here is what you must know about the Alpha-Fetoprotein test which is carried out during pregnancy.In pregnancy, the alpha-fetoprotein is a substance released by the foetus and enters the bloodstream of the mother. It is important to monitor the levels of alpha-fetoprotein in mother’s blood as the higher levels of it may indicate possibility of birth defects in the newborn or it may point towards other facts that are harmless.
It is important to get tested and take advise of the doctor and get other follow-up tests done that bring light to the cause of high AFP levels in the mother’s blood sample.
The Birth Defects that the AFP Test Points Towards
When a woman is pregnant, substances produced from the foetus mix in the blood stream of the mother.
Alpha-fetoprotein being one of them must be checked between the 15th and the 17th week of pregnancy. High levels of AFP in the bloodstream indicate problems like neural tube defects in the foetus such as Spina Bifidia, chromosomal problems such as Down Syndrome; also known as trisomy 21, and trisomy 18 or the Edwards syndrome. It also helps to detect omphalocele, a problem prevalent at birth in which part of the baby’s intestines stick out through the wall of the belly.
Other Possibilities that High AFP Level in Mother’s Blood Test Indicate
But sometimes even though high levels of AFP prevail, the baby may come out unscathed and the results of the sample may point towards two other possibilities that are not bad news at all. The high level of AFP usually increases between the 4th and the 6th month and may imply that the mother may be in the advanced stage of
pregnancy and the due date needs a recalculation. The other possibility may be that the mother may be carrying twins. The only way to find out would be to get an ultrasound done which would throw light on the actual situation.
Are AFP tests Reliable?
Also sometimes the AFP results may be wrong. The results may be false negative or false positive. False positive is when the results favour the possibility of a birth defect in the baby and it turns out otherwise, and false negative is when the result negates the possibility of birth defect and in reality the baby suffers the defect.
How to Ensure the Results?
The doctor may recommend a follow-up of ultrasound, a recalculated AFP to determine the new and probably earlier delivery date or possibility of twins or
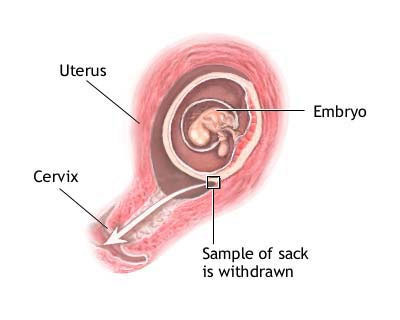
Amniocentesis or both to test the fluid surrounding the baby.
Should an AFP Test be conducted? What are the more reliable alternative tests to AFP?
The AFP test is not reliable either way though it is a harmless test physically. An AFP merely reflects at the possibilities of birth defects in the baby which would only be determined with follow-ups and timely routine checkups.
Ultrasounds conducted between the 18th and the 20th week of pregnancy has largely replaced the AFP to detect the abnormalities. Other tests that have replaced the AFP are the first trimester prenatal blood test conducted between the 9th and the 13th week and the nuchal translucency conducted between the 11th and the 13th week to detect the Down Syndrome in the baby.
So if the expecting mother gets a high or low level of AFP, she needs to remember that other routine tests are more reliable and dependable. And a high AFP may only announce a change in delivery date if not the arrival of twins. Timely prenatal tests must be conducted and it is highly important for the expecting mother to learn to relax through the pregnancy phase.
When is Alpha-Fetoprotein test or AFP test recommended during pregnancy? How is Alpha-Fetoprotein tests carried out? Are the results of Alpha-Fetoprotein test accurate? Discuss here.