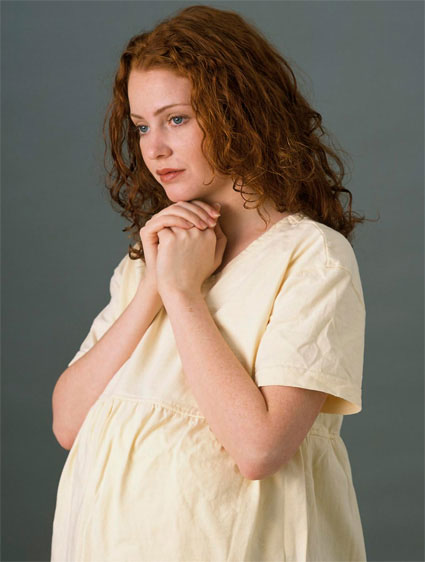
TB in pregnancy can only be managed with Tuberculosis drugs. Find out the effect of tuberculosis drugs during pregnancy.There are differences between developed and developing countries in the choice of anti-tuberculous agents and treatment schedules because of the cost and supervision of long term treatment. To allow for the possibility of bacterial resistance the treatment consists of 2-3 first lime agents such as ethambutol, rifampicin, etc.
Some TB drugs like ethambutol and isoniazad are safe. Others like rifampicin if used late in pregnancy can cause bleeding in newborn infants and mothers. If rifampicin is used in the last few weeks of pregnancy, vitamin K should be given to the mother and the newborn infant.
| Products: | Rifampicin |
| For Children: | Reduced dose necessary |
| For Pregnant Women: | Contra-indicated |
| For Breastfeeding Mothers: | Caution |
| Contra-indications*: | Hypersensitivity, severe liver disease |
| Caution: | Monitor blood counts in prolonged use |
Note* Pregnant women must not take any medicines without consulting a doctor.
Treatment for TB during Pregnancy
If you are opting for treatment for TB in
pregnancy, you need to consider the foetus developing inside. When planned carefully, treatment offered to you shall have positive effects on your unborn child as well. Proper planning is highly essential to reduce chances of congenital anomalies.
The American Thoracic Society (ATS) has issued certain guidelines about appropriate management of TB during pregnancy.
The initial stages of treatment shall be based on assessment of M tuberculosis strains along with the nature of resistance in the group. Empiric therapy is generally started with before arrival of clinical findings. In case the condition is not found very alarming, first line therapy is generally applied.
Treatment Procedures in Pregnancy
It is very essential to look for proper treatment when diagnosed with active TB in pregnancy. Even when you are diagnosed in the 1st stage, you may be suggested ethambutol, rifampin and isoniazid. Pyrazinamide is generally suggested to those with multi drug resistance. Streptomycin is known to have harmful effects on the foetus and thus is generally not suggested.
Following are the cases where strict preventive measures should be adopted during pregnancy.
- Those who are diagnosed with positive tuberculin skin who have risk factors associated with HIV infection, but has refused to go for the tests.
- Those who are pregnant and have come in touch with people with smear-positive for pulmonary tuberculosis.
- The pregnant women who went for tuberculin documented skin test conversion in the past 2 years.
Those who are pregnant and are at increased rate of isoniazid-induced hepatotoxicity are suggested isoniazid-induced hepatotoxicity on a monthly basis while undergoing the treatment. This shall continue for around 3 months into postpartum phase. The pregnant woman is administered pyridoxine while getting isoniazid.
TB Drugs and Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding can be continued safely in course of the preventive phase. In some cases your doctor may also suggest supplemental pyridoxine to the baby
breastfeeding.
There are safety concerns associated with the second line of medicines for the developing foetus. Thus, it is important to talk with the doctor about best safe measures before going forward with one in pregnancy.
Those who are treated with the first line of medicines, can safely breastfeed their children. Even though medicines in small amounts may mix with the
breastmilk, it shall cause no potential harm to the baby. According to doctors, it is important for women undergoing TB treatment to take vitamin B6 while breastfeeding.
Importance of Treatment for TB in Pregnancy
Those with active tuberculosis must go for treatment as early as possible. INH is suggested in the initial stages and then ethambutol is suggested for the next 2 months. There after a combination of RIF & INH are carried on daily for the rest of the 7 months. This is how the treatment is carried on for the 9 months of pregnancy.
Those with latent tuberculosis, INH are suggested twice a week for the whole course of pregnancy. As mentioned before, those on INH must also take B6 vitamin daily.
There is no need to despair if you are diagnosed with TB in pregnancy. There are plenty of medical facilities available that shall take good care of both of you. However, make sure to take your medicine regularly and visit your doctor in the scheduled appointments. Since, you would not want to invite any further trouble in pregnancy, do not forget to follow his instructions and enjoy your days in peace.
You must not hesitate to come up with questions that you might have about your unborn child or pregnancy. Your doctor shall be the right person to answer all your queries.
How to manage tuberculosis during pregnancy? How does tuberculosis affect pregnancy? What are side effects of tuberculosis drugs? Discuss here